Quick Exam Notes Science for Upper Secondary are specially compiled to help students prepare for important tests and examinations.
Clear Presentation Format
Notes are presented in point form for ease of understanding and systematic learning. Students will be able to review important concepts and examples quickly.
Useful Illustrations
A variety of diagrams, graphs and tables are included. Students will be able to understand concepts and processes easily through these helpful visual aids.
Contents
Section I: Measurement
CHAPTER 1: Physical Quantities, Units and Measurement
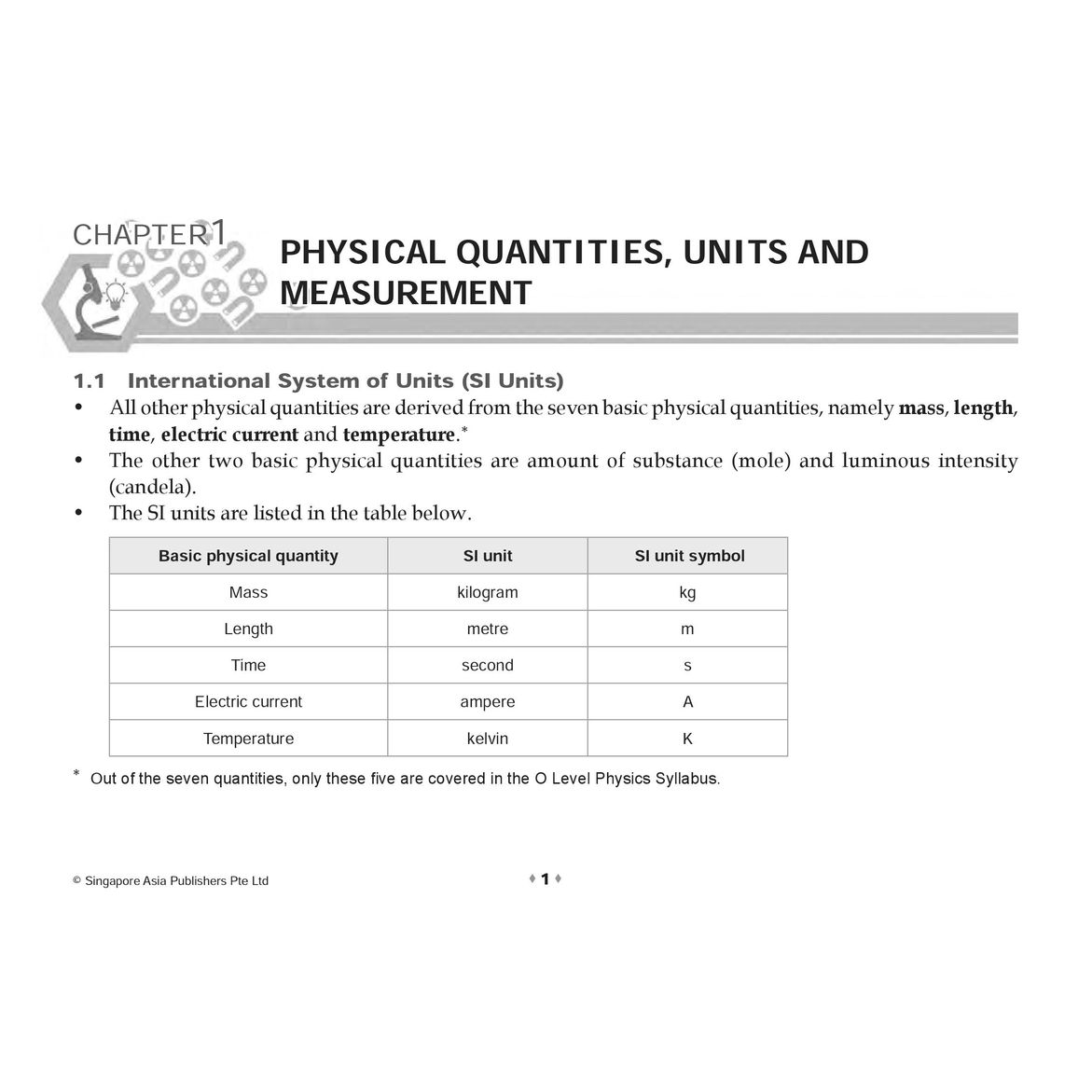
- 1.1 International System of Units (SI Units)
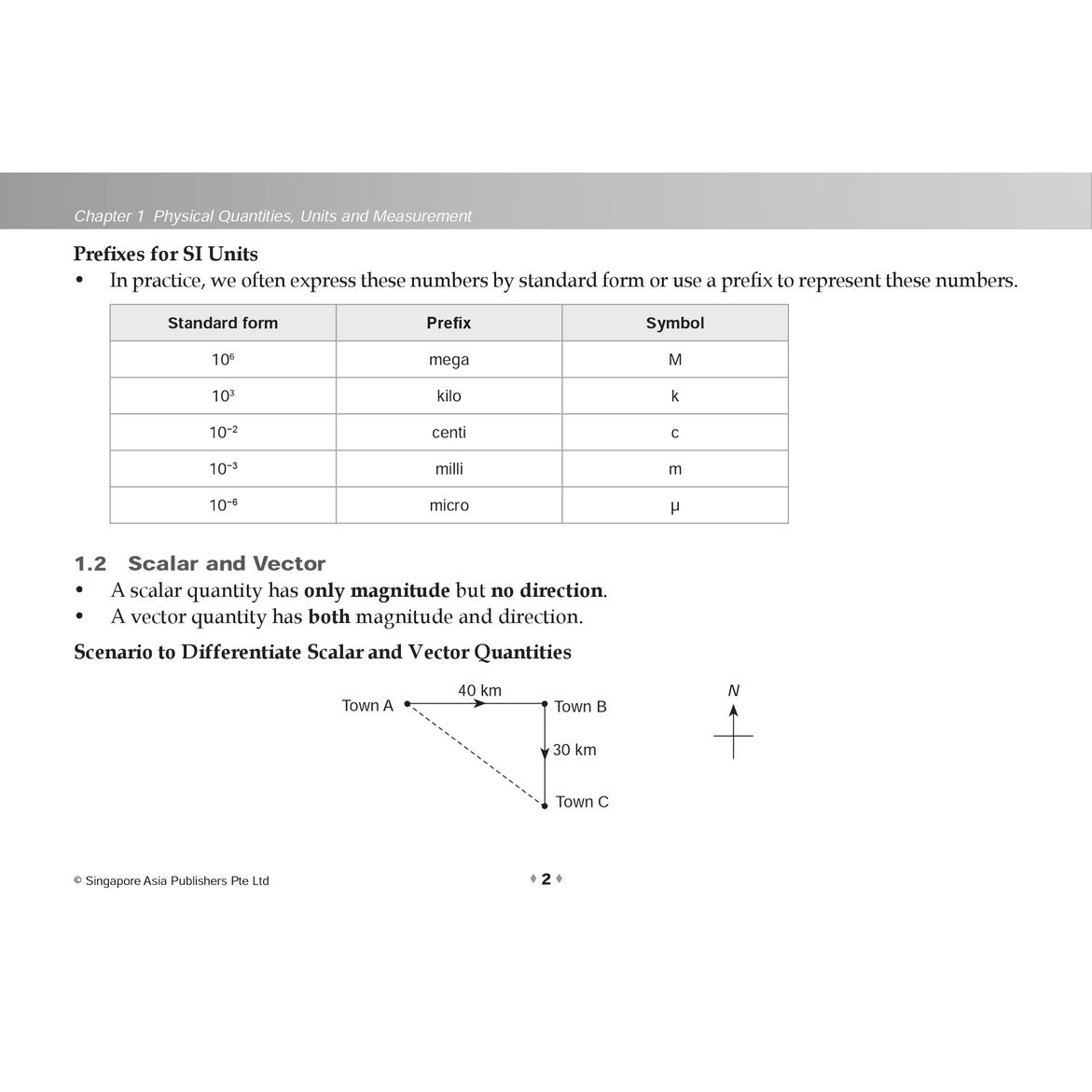
- 1.2 Scalar and Vector
- 1.3 Measuring Length
- 1.4 Measuring Time
- 1.5 Measuring the Volume of an Irregularly-shaped Object
Section II: Newtonian Mechanics
CHAPTER 2: Kinematics
- 2.1 Speed and Velocity
- 2.2 Displacement-Time Graph
- 2.3 Velocity-Time Graph
- 2.4 Acceleration Due to Gravity
CHAPTER 3: Dynamics
- 3.1 Definition of Force
- 3.2 Resultant Force
- 3.3 Newton’s Laws of Motion
- 3.4 Friction
- 3.5 Balanced Forces
- 3.6 Unbalanced Forces
CHAPTER 4: Mass, Weight and Density
- 4.1 Mass
- 4.2 Weight
- 4.3 Density
- 4.4 Experiment to Measure the Density of an Irregularly-shaped Object
CHAPTER 5: Turning Effect of Forces
- 5.1 Moment of a Force
- 5.2 Principle of Moments
- 5.3 Centre of Gravity (CG) of Regularly-shaped Objects
- 5.4 Stability
CHAPTER 6: Pressure
- 6.1 Pressure
- 6.2 Atmospheric Pressure
- 6.3 Liquid Pressure
- 6.4 Mercury Barometer
- 6.5 Manometer
CHAPTER 7: Work, Energy and Power
- 7.1 Work
- 7.2 Energy
- 7.3 Power
Section III: Thermal Physics
CHAPTER 8: Kinetic Model of Matter
- 8.1 States of Matter
- 8.2 Kinetic Theory of Matter
- 8.3 Brownian Motion
- 8.4 Pressure in Gas
CHAPTER 9: Transfer of Thermal Energy
- 9.1 Methods of Heat Transfer
- 9.2 Conduction
- 9.3 Convection
- 9.4 Radiation
- 9.5 Application of Heat Transfer – A Vacuum Flask
- 9.6 Experiments to Investigate Absorption and Emission of Radiation by Black and Silvery Surfaces
CHAPTER 10: Temperature
- 10.1 Temperature
- 10.2 Measuring Temperature
CHAPTER 11: Thermal Properties of Matter
- 11.1 Internal Energy
- 11.2 Heat Capacity and Specific Heat Capacity
- 11.3 Melting and Solidification
- 11.4 Boiling and Condensation
- 11.5 Latent Heat of Fusion and Specific Latent Heat of Fusion
- 11.6 Latent Heat of Vaporisation and Specific Latent Heat of Vaporisation
- 11.7 Evaporation
Section IV: Waves
CHAPTER 12: General Wave Properties
- 12.1 Waves
- 12.2 Wave Properties
- 12.3 Mechanical Wave Generator
- 12.4 Reflection and Refraction of Waves
CHAPTER 13: Light
- 13.1 Nature of Light
- 13.2 Reflection of Light
- 13.3 Refraction of Light
- 13.4 Total Internal Reflection and Critical Angle
- 13.5 Experiment to Demonstrate the Refraction of Light Through a Rectangular Glass Block
- 13.6 Types of Lenses
- 13.7 Ray Diagrams
CHAPTER 14: Electromagnetic Spectrum
- 14.1 Electromagnetic Spectrum
- 14.2 Common Properties of All Electromagnetic Waves
- 14.3 Examples of Uses of Electromagnetic Waves
CHAPTER 15: Sound
- 15.1 Nature of Sound
- 15.2 Transmission Medium for Sound
- 15.3 Audible Range
- 15.4 Reflection of Sound Waves – Echoes
- 15.5 Pitch
- 15.6 Loudness
Section V: Electricity and Magnetism
CHAPTER 16: Static Electricity
- 16.1 Atomic Structure
- 16.2 Charging by Friction
- 16.3 Electric Charges
- 16.4 Neutralising Charges
- 16.5 Charging Conductors by Induction
- 16.6 Gold Leaf Electroscope
- 16.7 Electric Field
- 16.8 Applications of Electrostatics
- 16.9 Hazards of Electrostatics
CHAPTER 17: Current of Electricity
- 17.1 Conventional Current
- 17.2 Electric Current
- 17.3 Electromotive Force (e.m.f.)
- 17.4 Potential Difference (p.d.)
- 17.5 Resistance
CHAPTER 18: D.C. Circuits
- 18.1 Circuit Symbols
- 18.2 Potential Divider
- 18.3 Thermistor
- 18.4 Light-dependent Resistor
CHAPTER 19: Practical Electricity
- 19.1 Practical Usage of Electricity
- 19.2 Electrical Power
- 19.3 Electric Energy
- 19.4 Calculating Electrical Consumption
- 19.5 Electrical Plug Wiring
- 19.6 Safe Use of Electricity
- 19.7 Dangers of Electricity
CHAPTER 20: Magnetism
- 20.1 Polarity
- 20.2 Magnetic Induction
- 20.3 Magnetism
- 20.4 Magnetisation and Demagnetisation
- 20.5 Magnetic Field
- 20.6 Properties and Applications of Magnets
CHAPTER 21: Electromagnetism
- 21.1 Magnetic Effect of a Current
- 21.2 Strength of Magnetic Field
- 21.3 Interactions Between Electric and Magnetic Fields
- 21.4 Magnetic Field Between Two Current-Carrying Conductors
- 21.5 Current-Carrying Rectangular Coil in Magnetic Field
- 21.6 Motion of Charged Particles in Magnetic Field
CHAPTER 22: Electromagnetic Induction
- 22.1 Electromagnetic Induction
- 22.2 Alternating Current (A.C.) Generator
- 22.3 Cathode Ray Oscilloscope
- 22.4 Closed-Core Transformer
- 22.5 Power Transfer in Transformer
- 22.6 Ways to Reduce Energy Loss in Power Transmission
APPENDIX: PHYSICS FORMULA LIST
ISBN : 9789814672931
Number of Pages : 152
Author : K. Low / Tay W. J. / Cheng Chung Yu